The Design Thinking Process: What it is & Why does it matter?
The user experience (UX) design process is a crucial part of creating a user-friendly experience for your product or service. By following the design thinking process in a few simple steps, you can ensure that your users have a positive experience with your company. In this blog, we will explore what design thinking is and each step of the design thinking process in detail. You will have a better grasp of how to apply design thinking to develop user-friendly experiences and how it contributes to better UI/UX designs at the conclusion of this blog.
Table Of Content
What is Design Thinking?
Design thinking is a human-centered approach to problem-solving that can be used to create user-friendly experiences. It is a process that begins with an understanding of the user’s needs and ends with a product or service that meets those needs.
The Five Steps of the Design Thinking Process
Design thinking is an iterative process that involves five steps, that starts with empathy and ends with testing, each step is essential in creating a user-friendly experience. The five steps are: empathize, define, ideate, prototype, and test. By following these 5 steps, you can create a product or service that your users will love.
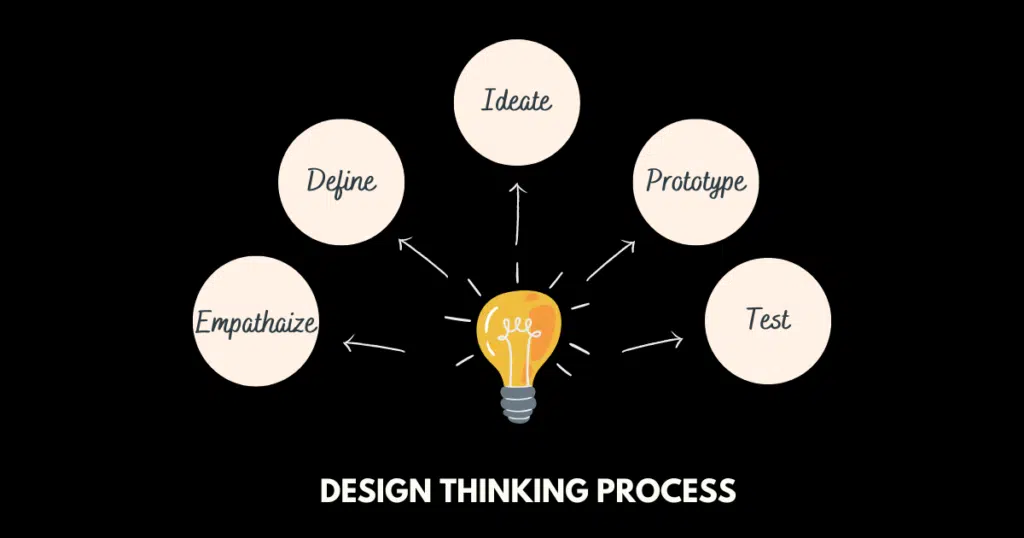
Step 1: Empathize
The first step of the design thinking process is to empathize with the people you are designing for. It’s important to understand their needs and motivations, as well as their challenges before you begin creating.
Step 2: Define
Next, you must define your target audience and their needs by asking questions like: What are they trying to accomplish? What are their goals or ambitions? Who are they? Where does this product or service fit into their lives?
Step 3: Ideate
Once you’ve defined your target audience, the next step in design thinking is ideating. This is where you get creative and come up with new ideas for your product. You can do this by brainstorming with a lot of collaboration between all involved parties (including non-designers), so that everyone has a voice in determining what makes sense and what doesn’t, but it’s important to focus on all aspects of the design process so that you don’t get stuck on one particular idea or solution.
Step 4: Prototype
The fourth step of design thinking is to prototype ideas. A prototype is a rough draft of a product or service that can help you test your idea and determine if it’s feasible. Prototyping takes time and effort, but it can be worth it when you’re trying to evaluate new ideas.
For example, if you want to sell a new product, you might create an online store with sample products that you can use as a template for your own products. You could also build a website where users can request products they need or want. This would help you determine which features are important before building out the rest of your site.
Step 5: Test
Once you have created a few different prototypes, it’s time to test them out against each other and against real-life objects in order for them to become better designs. Try changing colors or materials until you find one that works best for your product or design project.
How Design Thinking Differs from Traditional Product Development
Design thinking and agile methodologies have been around for a long time. However, they are still not commonly applied in product development. It is a relatively new discipline that has been gaining more traction recently. The main difference between traditional design and design thinking is that with traditional design, you have a specific product or service in mind.
In contrast, design thinking is a different way of approaching product development. It’s not about creating something new, but about creating something better than what you have before. The idea behind it is to challenge yourself and your teammates as designers and developers to think differently about your product.
Design Thinking starts with the problem-solution-constraints framework. And then it uses this framework to create solutions for other problems as well. The process starts with the first meeting where you ask yourselves: What are we trying to achieve? What problem do we want to solve? How will our solution help our users? We then design a prototype of how the solution will work and test it with potential users. Once we have enough evidence that this prototype works, we move on to the next step: Designing the actual product.
The Benefits of Design Thinking
The main benefit of using design thinking is that it helps you solve problems in an unconventional manner instead of doing what everyone else does or what is expected by the market at large. This approach helps you come up with solutions that are much more innovative and creative than those suggested by mainstream methods like user research or focus groups.
Design thinking has been used to create some of the most popular products and services in the world, such as the Apple iPhone and the Tesla Model S. But it can also be used to solve more mundane problems, such as how to make a better cup of coffee or how to design a more user-friendly website.
There are many benefits to using design thinking, including that it:
- Encourages creativity and out-of-the-box thinking
- Helps to build a deep understanding of the user
- Helps to create solutions that are user-friendly and meet the needs of the customer
- It’s a process that all stakeholders collaborate on.
Design thinking: a non-linear process
Design thinking is a cyclical process, like a spiral. It’s not just a linear process, where you are following some sort of steps or stages. It’s critical to realize that the design process is not a collection of guidelines that you must adhere to. Understanding your consumers’ motivations and how to satisfy them with your offering are more important.
Due to the UX design approach’s enormous versatility, it may be applied in any situation. The path that must be followed is not necessarily linear. It may even be pretty hectic at times. For instance, you could have a fantastic concept for a brand-new website or app, only to discover that you can’t implement it without sacrificing other features or functionality due to financial constraints. This implies that you will have to change one aspect of your strategy. In this case, you have to start from the middle of the spiral and go out. For example, you can start from the define stage and go towards the idea generation stage. The key is to create and iterate designs quickly and test them with potential users to get feedback.
FINAL VERDICT :
If you have read this far, I really appreciate it. I hope you enjoyed reading this article on “The Design Thinking Process: What it is & Why does it matter?”, If yes, then don’t forget to spread the word about it, Click your favorite social media icon below to share this content. Signing off sowmiyavenkatesan611@gmail.com






